Introduction
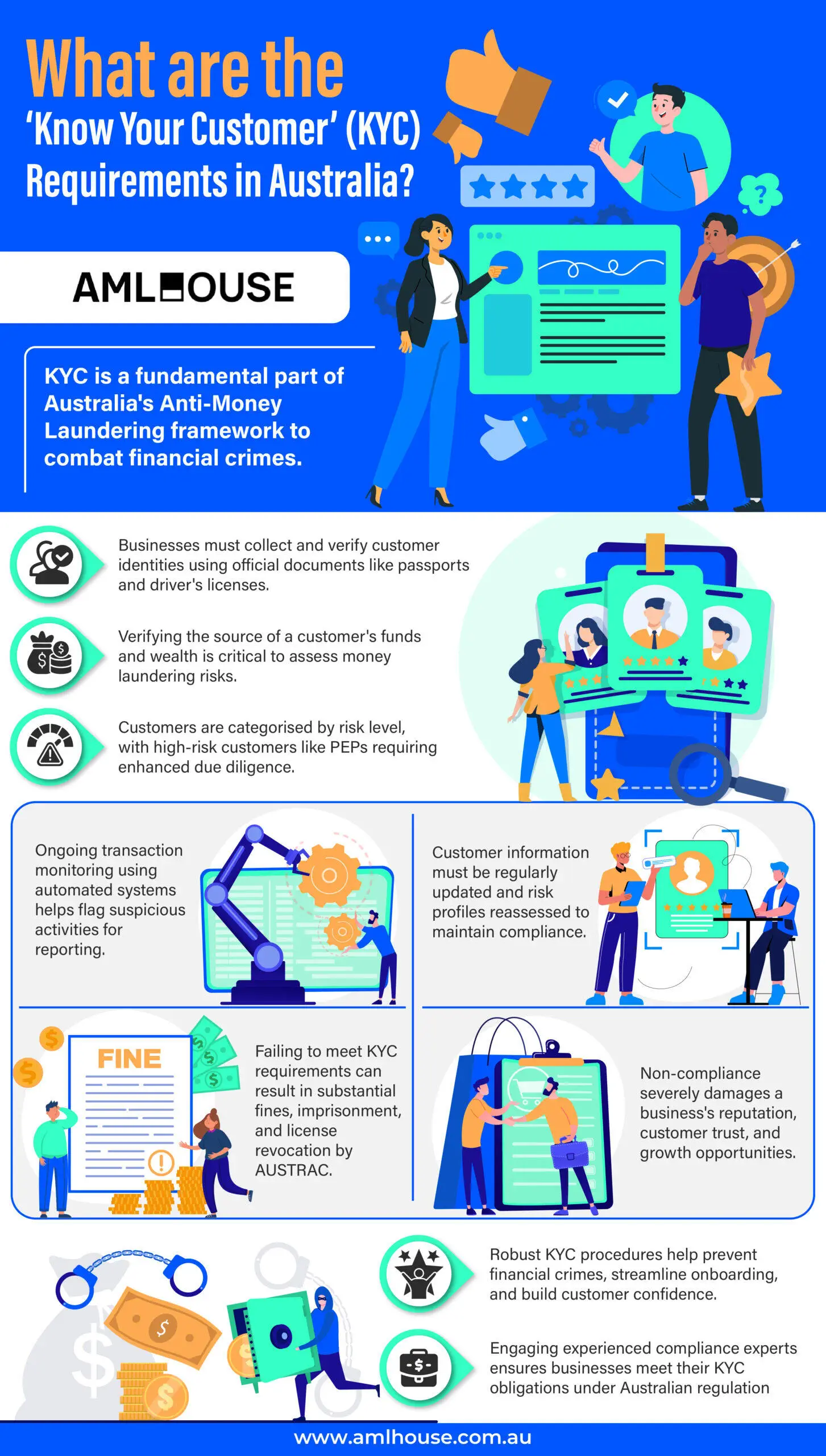
Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations in Australia are fundamental to the country’s Anti-money Laundering (AML) framework, mandating businesses to collect and verify customer information in alignment with Financial Action Task Force (FATF) standards. These requirements are crucial for mitigating financial crimes, ensuring regulatory compliance, and safeguarding the integrity of Australia’s financial system.
Implementing KYC involves comprehensive customer identification, verification processes, and continuous monitoring overseen by regulators such as Australian Transaction Reports and Analysis Centre (AUSTRAC). This overview underscores the significance of KYC regulations in preventing money laundering and terrorism financing, setting the stage for a detailed exploration of Australia’s specific KYC requirements and compliance strategies.
Importance of KYC in AML Compliance
The Role of KYC in Mitigating Financial Crimes
KYC procedures are fundamental in combating various financial crimes, including money laundering, terrorist financing, fraud, and identity theft. By verifying the identities of customers, financial institutions can significantly reduce the risk of these illicit activities infiltrating their systems.
Key ways KYC mitigates financial crimes include:
- Preventing Money Laundering: Accurate customer identification makes it difficult for criminals to disguise illegally obtained funds as legitimate income.
- Stopping Terrorist Financing: KYC helps in identifying individuals who may be funding terrorist activities, thereby blocking their financial transactions.
- Reducing Fraud: By thoroughly verifying customer information, KYC processes help in detecting and preventing fraudulent activities such as identity theft and unauthorised transactions.
- Enhancing Security: Verifying customers’ identities protects both the financial institution and legitimate customers from unauthorised access and fraudulent transactions.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Adhering to KYC requirements is not only a best practice, but also a legal obligation under Australia’s AML/CFT Act 2006 (Cth). Financial regulators such as AUSTRAC, Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC), and Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) enforce these standards to maintain the integrity of the financial system.
Key aspects of ensuring regulatory compliance through KYC include:
- Legal Obligations: Australian firms must implement KYC procedures as part of their AML/CFT (Countering the Financing of Terrorism) programs to comply with the AML/CFT Act 2006 (Cth).
- Regulatory Oversight: AUSTRAC oversees and enforces compliance with AML and CFT regulations, ensuring that financial institutions adhere to KYC standards.
- Risk-Based Approach: Financial institutions must assess the risk associated with each customer and apply appropriate due diligence measures based on their risk profiles.
- Record-Keeping Requirements: Firms are required to maintain detailed records of customer identification and verification processes for at least seven years, facilitating audits and investigations.
By maintaining robust KYC practices, financial institutions not only comply with legal standards but also contribute to a safer and more secure financial environment.
Get Your Free Initial Consultation
Request a Free Consultation with one of our experienced AML Lawyers today.
KYC Regulations in Australia
Customer Identification and Verification
In Australia, KYC involves verifying the identity of both individual and non-individual customers before providing any designated services. Businesses must collect and verify personal information using official documents such as:
- Passports
- Driver’s licenses
- Proof of address
For non-individual entities like companies, firms must confirm the company’s existence and identify its beneficial owners, ensuring transparency in ownership structures. This robust verification process is essential to prevent financial crimes and maintain the integrity of the financial system.
Source of Funds and Wealth Verification
Verifying the source of funds (SoF) and source of wealth (SoW) is a critical component of KYC in Australia. Businesses are required to assess where a customer’s funds originate and examine their overall financial background to identify potential risks associated with money laundering or terrorism financing. This involves gathering detailed information about a customer’s financial activities, including:
- Their occupation
- Investments
- Inheritance
- Any other relevant financial sources
By understanding the origin of a customer’s wealth, firms can better evaluate the legitimacy of their financial transactions and mitigate associated risks.
Customer Risk Assessment
A risk-based approach is essential for effective customer risk assessment under Australia’s KYC framework. Businesses must evaluate the potential risk each customer poses based on various factors such as:
- Geographical location
- Nature of their business
- Transaction volumes
- Financial behaviour
High-risk customers—including politically exposed persons (PEPs) or those from high-risk jurisdictions—require enhanced due diligence measures to ensure thorough scrutiny. By categorising customers according to their risk profiles, firms can implement appropriate controls and monitoring strategies to manage and mitigate potential threats related to financial crimes.
Ongoing Monitoring and Due Diligence
Transaction Monitoring
Effective transaction monitoring is vital for identifying suspicious activities that may indicate financial crimes such as money laundering or terrorist financing. Firms must implement systems to continuously review customer transactions for unusual patterns or behaviours. When suspicious activity is detected, it is essential to report these findings to AUSTRAC through Suspicious Matter Reports (SMRs). Key elements of transaction monitoring include:
- Automated Monitoring Systems: Utilising software to track and flag transactions that deviate from a customer’s typical behaviour.
- Threshold Settings: Establishing specific limits for transaction sizes and frequencies that trigger alerts.
- Review Procedures: Conducting thorough investigations of flagged transactions to determine their legitimacy.
- Timely Reporting: Ensuring that all suspicious activities are reported to AUSTRAC promptly to comply with regulatory obligations.
Updating Customer Information
Keeping customer information up-to-date is crucial for maintaining effective risk management and compliance with AML regulations. Regularly updating customer data helps in reassessing risk profiles and ensures that all records reflect the current status of the customer. The processes involved in updating customer information include:
- Periodic Reviews: Scheduling regular intervals to verify and update customer details, such as contact information and beneficial ownership.
- Re-Verification Procedures: Implementing steps to reconfirm identities when significant changes occur, such as alterations in business structure or ownership.
- Risk Reassessment: Continuously evaluating the risk level associated with each customer based on updated information.
- Documentation: Maintaining accurate and comprehensive records of all updates and verifications for auditing and compliance purposes.
Get Your Free Initial Consultation
Request a Free Consultation with one of our experienced AML Lawyers today.
Compliance and Penalties for Non-Compliance
Civil and Criminal Penalties
Failing to comply with KYC requirements in Australia can result in significant civil and criminal penalties imposed by AUSTRAC.
- Fines: AUSTRAC has the authority to impose substantial fines on reporting entities that fail to meet their AML/CFT obligations. The size of the fine varies based on the severity and nature of the non-compliance.
- Imprisonment: In cases where non-compliance is intentional or part of a broader criminal scheme, individuals within the non-compliant entity may face imprisonment.
- License Revocations: AUSTRAC can suspend or revoke the operating licenses of financial institutions or other reporting entities that repeatedly or egregiously fail to comply with AML/CFT requirements.
Reputational and Business Impact
Non-compliance with KYC requirements can severely damage a business’s reputation, leading to the loss of customers and business opportunities.
- Loss of Customer Trust: Customers may lose confidence in a business that fails to adhere to KYC regulations, perceiving it as unreliable or insecure.
- Financial Losses: Beyond fines and penalties, businesses may experience financial setbacks due to a reduced customer base and diminished business opportunities following reputational harm.
- Operational Disruptions: Enforcement actions by AUSTRAC, such as license suspensions or revocations, can disrupt business operations and lead to inefficiencies.
Failure to comply with KYC requirements not only exposes businesses to legal and financial risks but also undermines their credibility and market position.
Benefits of Being KYC Compliant
Risk Mitigation and Fraud Prevention
Implementing KYC compliance offers significant advantages in reducing financial risks and preventing fraudulent activities. By thoroughly verifying customer identities, businesses can:
- Prevent Money Laundering: Accurate customer identification makes it difficult for criminals to disguise illegally obtained funds as legitimate income.
- Stop Terrorist Financing: KYC processes help identify individuals who may be funding terrorist activities, thereby blocking their financial transactions.
- Reduce Fraud: By ensuring that customers are who they claim to be, KYC procedures help detect and prevent fraudulent activities such as identity theft and unauthorised transactions.
- Enhance Security: Verifying customer information protects both the financial institution and legitimate customers from unauthorised access and fraudulent transactions.
Operational Efficiency and Customer Trust
Efficient KYC compliance not only enhances security but also streamlines business operations and builds trust with customers. Key benefits include:
- Streamlined Customer Onboarding: With verified customer data readily available, firms can open accounts and offer services more efficiently, reducing administrative costs and speeding up time-to-market for new products.
- Improved Customer Experience: Automated KYC solutions enable faster and more accurate verification processes, enhancing the overall customer experience by minimising delays and simplifying account setup.
- Enhanced Trust and Reputation: Robust KYC standards build trust and integrity, attracting and retaining clientele. Customers are more likely to engage with businesses that demonstrate a commitment to security and transparency.
- Efficient Risk Management: By categorising customers based on risk profiles, businesses can allocate resources and monitoring efforts more effectively, ensuring that high-risk customers receive the necessary attention to mitigate potential threats.
By maintaining KYC compliance, businesses not only adhere to regulatory standards but also create a safer and more reliable environment for their customers, fostering long-term trust and operational success.
Conclusion
KYC plays a pivotal role in AML compliance by ensuring that businesses thoroughly identify, verify, and monitor their customers. Implementing robust KYC requirements in Australia helps mitigate the risks of money laundering, terrorism financing, and other financial crimes, thereby safeguarding both businesses and the financial system.
Adhering to Australian KYC regulations is essential not only for legal compliance, but also for maintaining trust with clients and protecting your organisation from significant penalties and reputational damage. To ensure your business meets all KYC obligations, contact our experienced compliance team today. Our specialised experts in Australian KYC regulations are ready to provide you with tailored solutions and support to enhance your AML compliance efforts.
Frequently Asked Questions
The core components of the KYC process include customer identification and verification, source of funds and source of wealth verification, and customer risk assessment.
Documentation required for customer identification includes official documents such as passports, driver’s licenses, proof of address for individuals, and company registrations, including the full company name, Australian Company Number (ACN), or Australian Registered Body Number (ARBN) for non-individual entities.
KYC helps prevent financial crimes by verifying customer identities, which mitigates risks of money laundering, terrorist financing, fraud, and identity theft, ensuring that illegal activities are less likely to infiltrate financial systems.
Penalties for non-compliance with KYC requirements in Australia include substantial fines, potential imprisonment for individuals, license suspensions or revocations, and significant reputational damage to businesses.
Businesses should address discrepancies by collecting additional information from customers, conducting thorough investigations, and reporting suspicious activities to the AUSTRAC as part of their risk-based systems and controls.
AUSTRAC oversees and enforces KYC compliance by providing guidance, monitoring financial institutions, and requiring the reporting of suspicious activities, ensuring that businesses adhere to AML/CFT regulations.
Yes, KYC processes can be automated, offering benefits such as faster and more accurate customer verification, enhanced operational efficiency, reduced compliance costs, and improved customer experience through streamlined onboarding.
Records of customer information must be maintained for the duration of the business relationship and for at least seven years after the provision of any designated services has ceased.
If a business suspects a customer of money laundering, it should immediately report the suspicious activity to AUSTRAC by submitting a Suspicious Matter Report and undertake enhanced customer due diligence to further investigate and mitigate the risk.